Biosciences, Biotechnology
Development of innovative tools for tackling ticks and the diseases they transmit in the context of climate change
The new research project ResTick, aiming to study and address ticks as vectors of pathogens that pose a threat to public health and livestock, will be implemented by the Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB) of the Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas (FORTH), with a budget of 6 million euros, funded by the European Commission.
International scientific collaboration reveals how intermittent fasting regulates ageing through autophagy
Recent research at the Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB) of the Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas (FORTH), at the Paris Cité University, and at the University of Graz, published today in the premier international science periodical Nature Cell Biology, sheds light on the mechanism through which spermidine regulates autophagy, a process that ensures the recycling of components within the cell, to promote the anti-ageing effects of intermittent fasting.
Of bantam brains and fancy footwork: bioinformatics tools help reveal complexity of avian evolution
In 2014 the Science journal featured an article on the bird tree of life, mentioning the essential role of algorithms and supercomputers that enable modern research in evolutionary biology for all types of living beings. Now, a decade and a giant leap in tool development later, part of the team that coordinated the computer analyses at that time co-authored another paper in Nature on the complexity of avian evolution.
Greek researchers from FORTH, NKUA and Harvard University reveal a new mechanism that regulates intestinal stem cells
In an article published recently at the high-impact journal Nature Communications, researchers from NKUA, FORTH-IMBB, and Harvard University, led by Prof. Aristides Eliopoulos of NKUA and postdoctoral researcher Dr. Zoe Veneti of FORTH-IMBB, reveal a new mechanism that regulates the proliferation and differentiation of intestinal stem cells.
Prestigious ERC Consolidator Grant awarded to FORTH Researcher Dr. Panagiotis N. Moschou
Panagiotis N. Moschou, Researcher at the Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB) of the Foundation for Research and Technology – Hellas (FORTH) and Associate Professor at the Department of Biology, University of Crete is awarded a Consolidator Grant from the European Research Council (ERC).
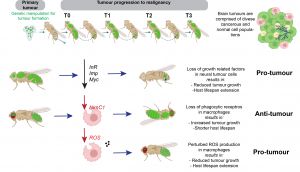
New study reveals the mechanisms that drive neural tumour progression to malignancy
A new research study FORTH-IMBB, published in the international peer reviewed science journal PNAS, reveals how cancer cell intrinsic mechanisms and interactions with the microenvironment shape brain tumour growth and progression to malignancy.
New study reveals a key role of mRNA metabolism determinants in ageing and disease, through the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and function
The new findings highlight the importance of mRNA storage and degradation, near mitochondria, as a mechanism for maintaining cellular and organismal homeostasis
FORTH researcher, Prof. Electra Gizeli, new elected member of the European Organization for Molecular Biology (EMBO)
This international distinction is awarded based on outstanding contribution to science and advancement of life sciences, through high-level innovative research and achievements.
A pivotal International Neuroscience Conference hosted in Crete
The prestigious International Neuroscience Conference of the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO), entitled "Cell Biology of the Nervous System", was held at the Fodele Beach Hotel, in Crete, from 8 to 11 May 2023.
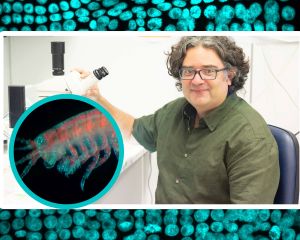
Prestigious HFSP Research Grant awarded to FORTH Researcher Dr. Anastasios Pavlopoulos
Anastasios Pavlopoulos, Principal Researcher at the Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology of the Foundation for Research and Technology – Hellas (IMBB-FORTH) is awarded a Research Grant from the 2023 Human Frontiers Science Program. HFSP promotes international collaboration in basic research focused on the elucidation of the sophisticated and complex mechanisms of living organisms.
Page:123 | Next >